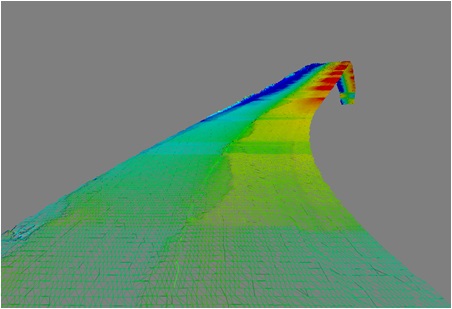
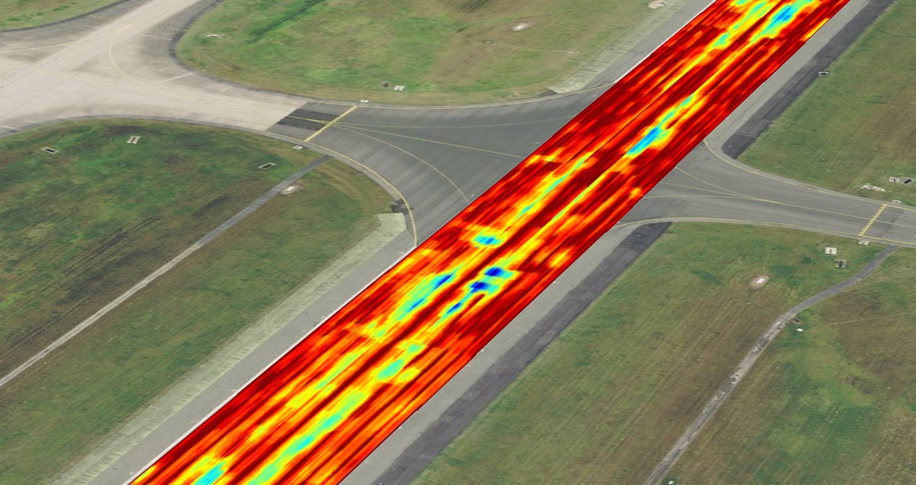
3D NM-GPR
What is GPR?
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) is a subsurface imaging technique that uses ultrawideband electromagnetic (EM) signals to investigate dielectric materials like soil, asphalt, crushed rock, timber, and ice.
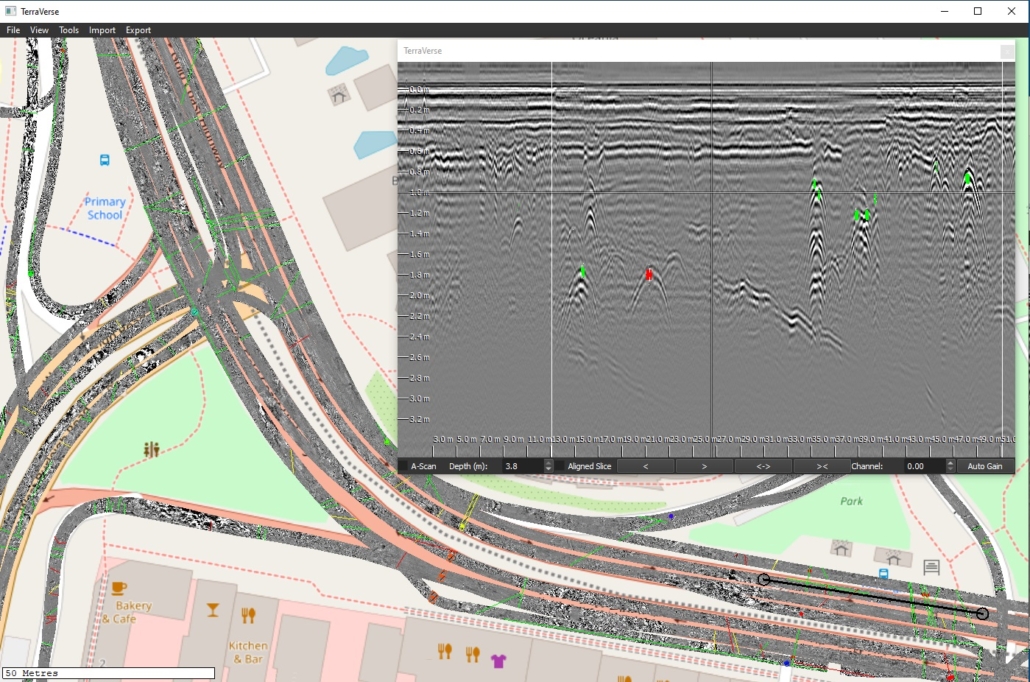
Within civil engineering, GPR is commonly used to locate subsurface utilities, map reinforcing steel, detect voids or defects, and determine as-built details of roads, bridges, and airport pavements ahead of upgrade and remedial works.
Why 3D?
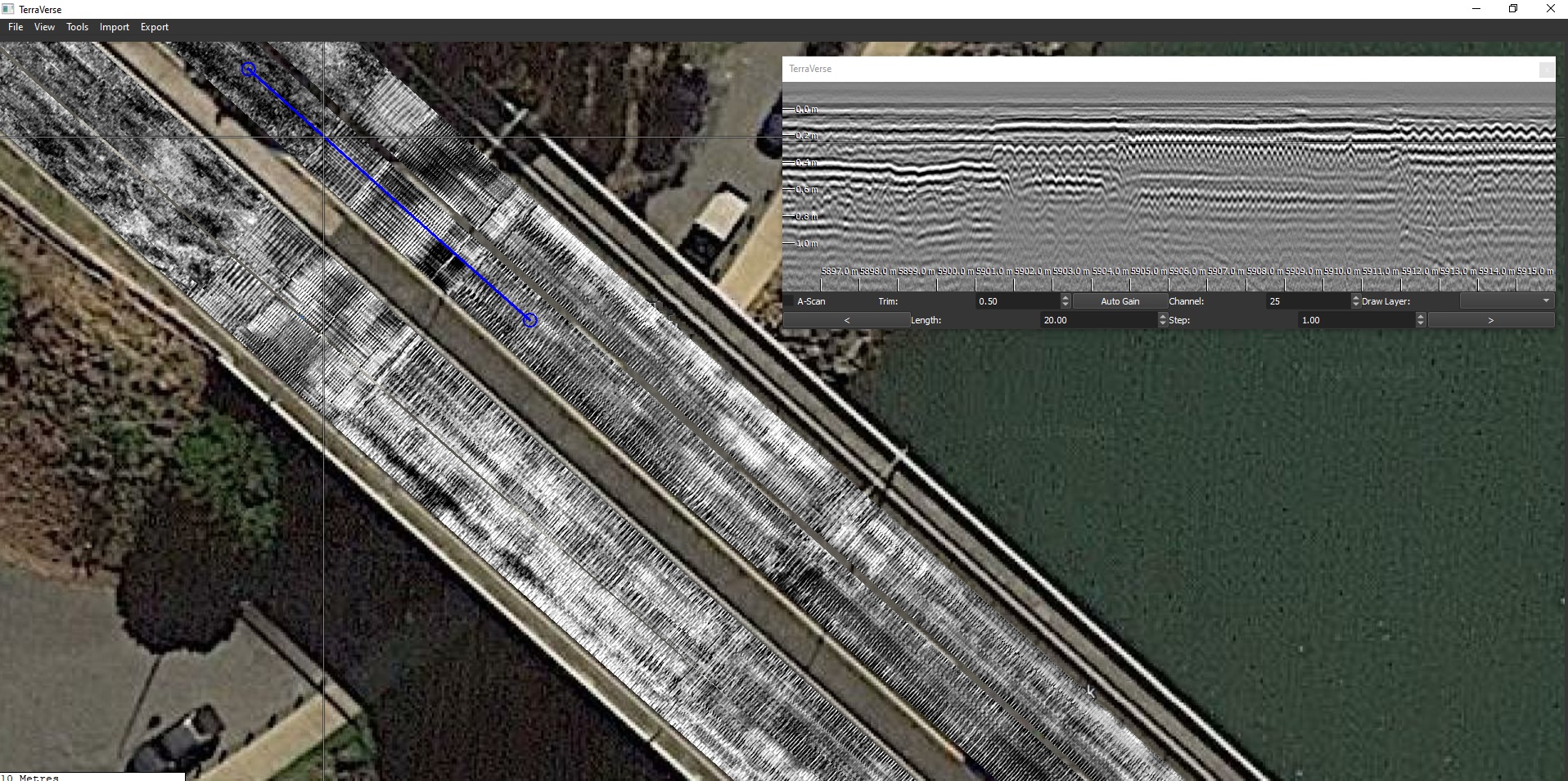
Most GPRs are simple 2D systems. These gather a single vertical slice of data along a path. A 3D volume of subsurface data can be created in software by combining multiple 2D scans gathered along a grid pattern. The 3D dataset can then be sliced vertically or horizontally to reveal subsurface features at various X-Y positions and depths. While effective for small scales, the approach quickly becomes too slow and impractical for large sites.
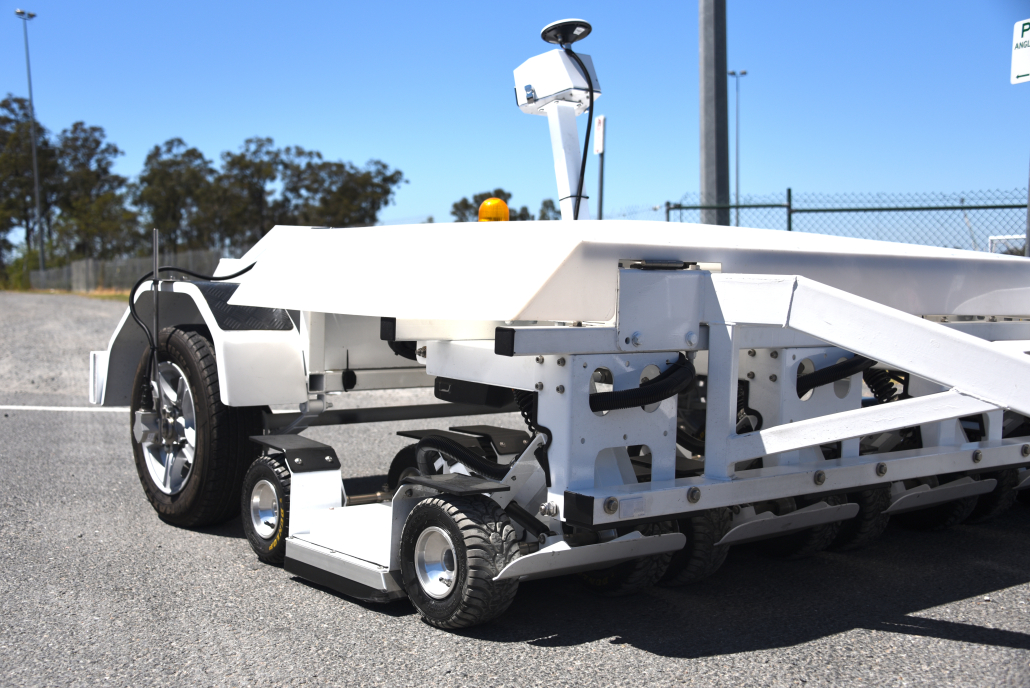
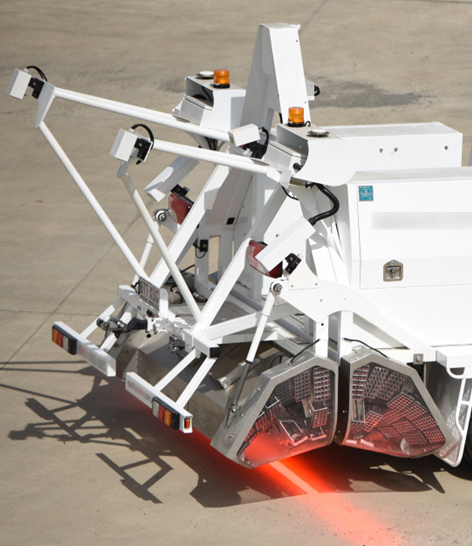
This is where dedicated 3D GPR systems step in. They gather a series of 2D GPR profiles across an antenna array, which greatly speeds up the data collection process. Multiple 3D scans can then in turn be merged to create very large data volumes covering complex sites such as roads, bridge decks, airport runways and parks in their entirety.
What is Noise-Modulated GPR?
Noise-Modulation refers to a signal modulation approach used in some GPR systems. Like impulse and stepped-frequency modulation techniques, the approach emits ultrabroadband signals and records the strength and timing of returning echoes. However, rather than emitting pulses or narrowband tones like these other systems, noise-modulated GPRs transmits a special type of coded signal whose autocorrelation is pulse-like. The strength of returning echoes is measured with respect to elapsed time, and the measured signal is cross-correlated with the emitted signal to produce the A-scan (“trace”) profiles.
Is NM-GPR the same thing?
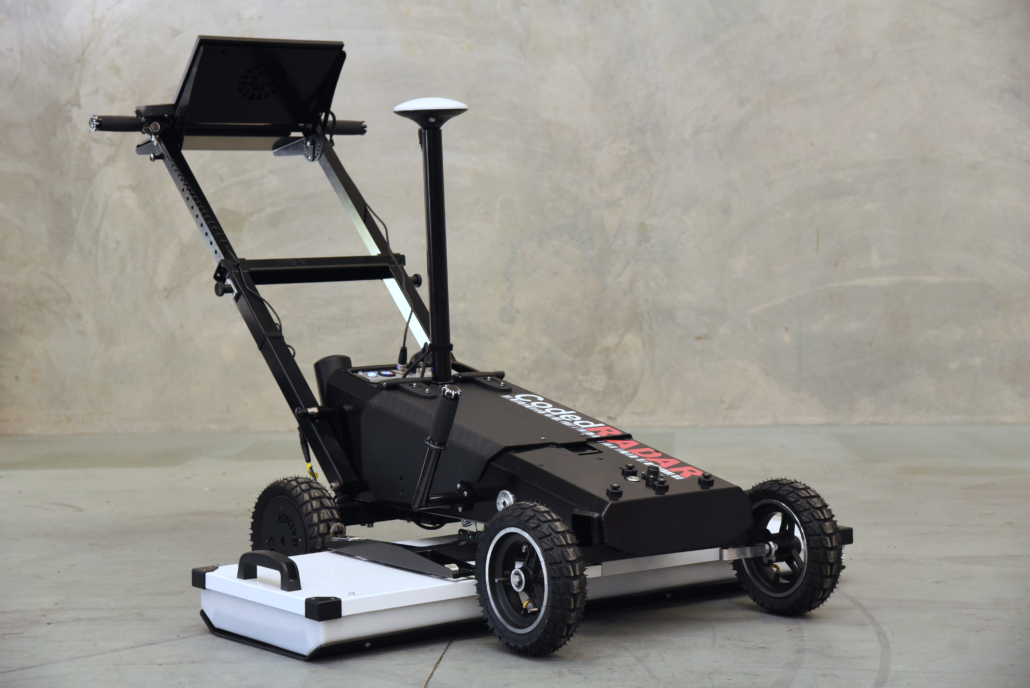
Partially. NM-GPR refers to a particular implementation of Noise-Modulated GPR developed by CodedRADAR. In addition to using coded signals, NM-GPR uses a radically different approach to GPR hardware and sampling. These differences sets NM-GPR hardware apart, enabling it to far outperform conventional 3D GPR technologies in several respects.
Why use a different approach?
Collecting fast, high-frequency 3D GPR data pushes hardware to its limits. At higher collection speeds, conventional systems often struggle to keep up with the huge number of required A-scan measurements. Regulatory limits on the strength and speed of GPR transmissions make the challenge even tougher—particularly in the 960–1610 MHz range, where imaging detail is better but restrictions are strictest. As a result, conventional 3D GPR equipment must either scan more slowly, spread out measurements, compromise imaging depth, or operate at lower frequencies—reducing resolution.
NM-GPR systems overcome these limitations with a fundamentally different design. Using unique coded transmission signals and multiple ultra-fast samplers, they capture A-scan measurements thousands of times faster than traditional GPR. Their compliant, noise-like transmissions allow NM-GPR equipment to operate across the frequency spectrum—including the more sensitive 960–1610 MHz range—delivering finer imaging detail without slowing down or losing penetration depth. And with rugged, ground-coupled 3D arrays, they avoid the near-surface image degradation common to air-coupled systems.
The result is blisteringly fast, high-detail, and highly reliable 3D GPR performance—free from the capacity limits of conventional technologies. For rapid, high-fidelity subsurface imaging, NM-GPR stands unmatched.
Surface + subsurface
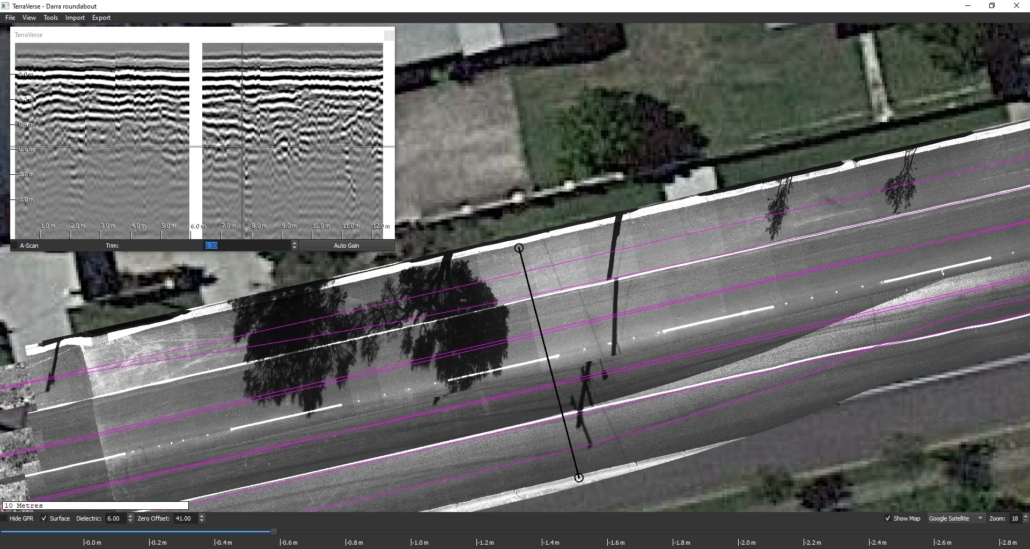
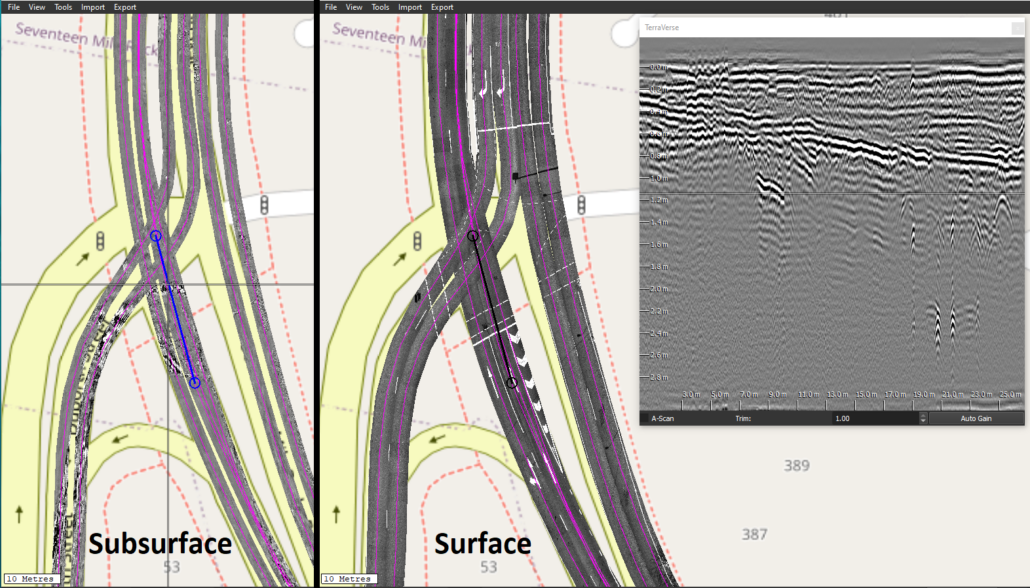
In addition to gathering 3D NM-GPR data, the Kerberos™ and Lynx systems can also capture geolocated surface imagery in the same pass. This provides a wealth of benefits for site investigations, including:
- Detailed snapshot: Provides a detailed record of current surface conditions throughout a site, to document or monitor changes over time.
- Relate cause and effect: Compare the location of subsurface defects and subsurface features or changes that may be causing them.
- Better site context: Use positions of manholes, pits, drainage inlets, bridge joints and other surface features to better inform & guide interpretation of 3D GPR data.
- Reliable positioning: As the surface and subsurface images are synchronized, it is possible to locate subsurface features by measuring their location relative to surface features. This feature is particularly useful for locating voids or defects within ‘urban canyons’ where GPS reception is often unreliable.
TerraVerse™
CodedRADAR’s TerraVerse™ software enables 3D NM-GPR and surface imagery data from hundreds of scans to be combined into large geospatially-corrected mosaics. This enables large assets such as roads, bridges, airports, ports, parks, gas stations, carparks to be covered in detail and later viewed and analysed as one model, for a holistic understanding of surface and subsurface features.
Auxiliary sensors
For more than 15 years we have created systems that integrate 3D NM-GPR with cameras and a variety of off-the-shelf and custom sensors. This includes sensors used for transverse laser profiling (e.g. measuring ruts), inertial measurement of vehicle motion (IMU), illuminated road surface imaging (i.e. for site context; mapping surface defects), roughness measurements (IRI), LiDAR, and a patented photometric stereo technique.
When you need advanced sensors that complement and make better use of 3D GPR data, CodedRADAR is your one-stop-shop.